Recommended Product Selection for Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS) Systems
What is Distributed Acoustic Sensing?
Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS) is an optical instrument that uses optical fiber as a sensor for sound vibration sensing. The system uses a single optical fiber to simultaneously monitor sound vibration and transmit the signal.
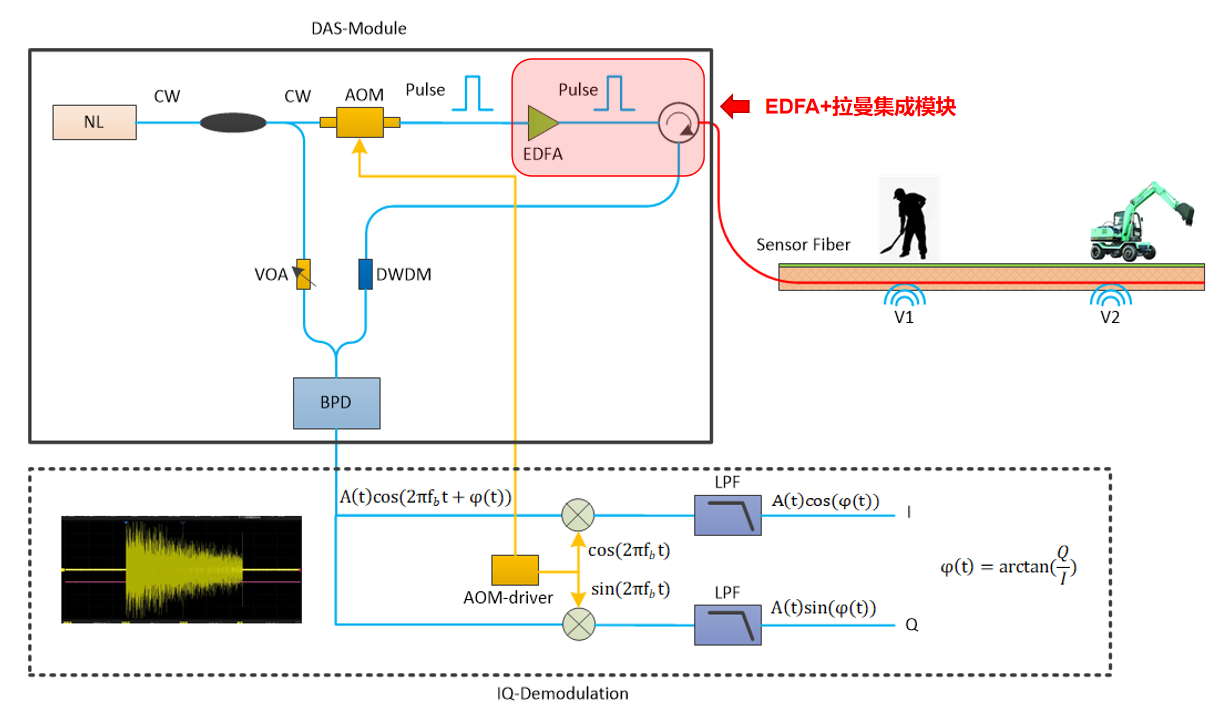
Distributed Acoustic Sensing Principle
The principle of distributed acoustic sensing system is to use the phase of coherent backscattered Rayleigh light rather than light intensity to detect signals such as sound vibrations in the audio range. Not only can the magnitude of the phase amplitude be used to provide information on the intensity of sound vibration events, but also linear quantitative measurements are used to achieve the acquisition of information on the phase and frequency of sound vibration events.
Distributed acoustic sensing schematic
How to Build Your Own DAS System
Enterprise users
Enterprise users require complete solutions, so they typically need software systems in addition to hardware. For such scenarios, we recommend our DAS integrated systems, as they feature fully integrated hardware. Simply plug in the fiber optic cables to get started—users only need to develop software algorithms tailored to their specific application scenarios.
Enterprise users who require their own chassis (brand)
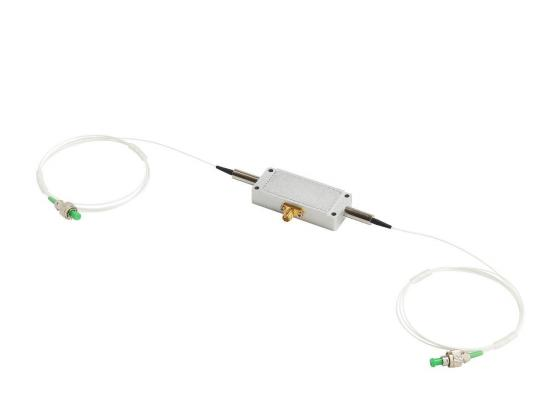
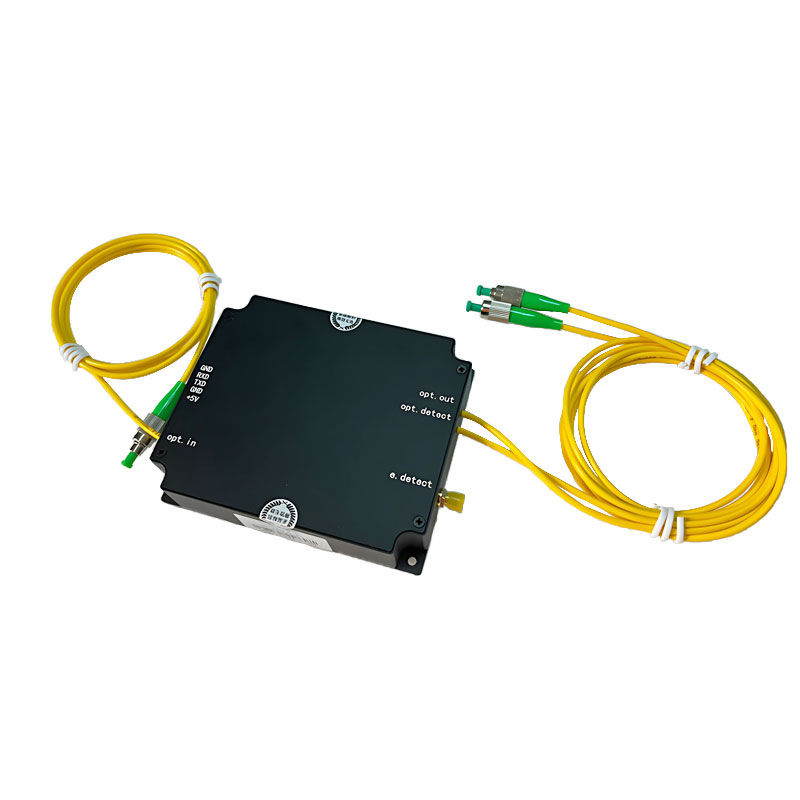
Enterprise users who need to build their own DAS equipment chassis can choose to integrate using DAS integrated modules and data acquisition cards. We offer standard DAS modules, enhanced DAS modules, and PCIe data acquisition cards with Ethernet/fiber ports. Users can select components based on their specific requirements.
Users for scientific research
Research clients often wish to understand and become familiar with the internal implementation principles and component structure of DAS systems, and may require modifications to the DAS optical path. For such users, our DAS system hardware module separation solution is available.