Distributed Acoustic Sensing Topic Page
What is Distributed Acoustic Sensing?
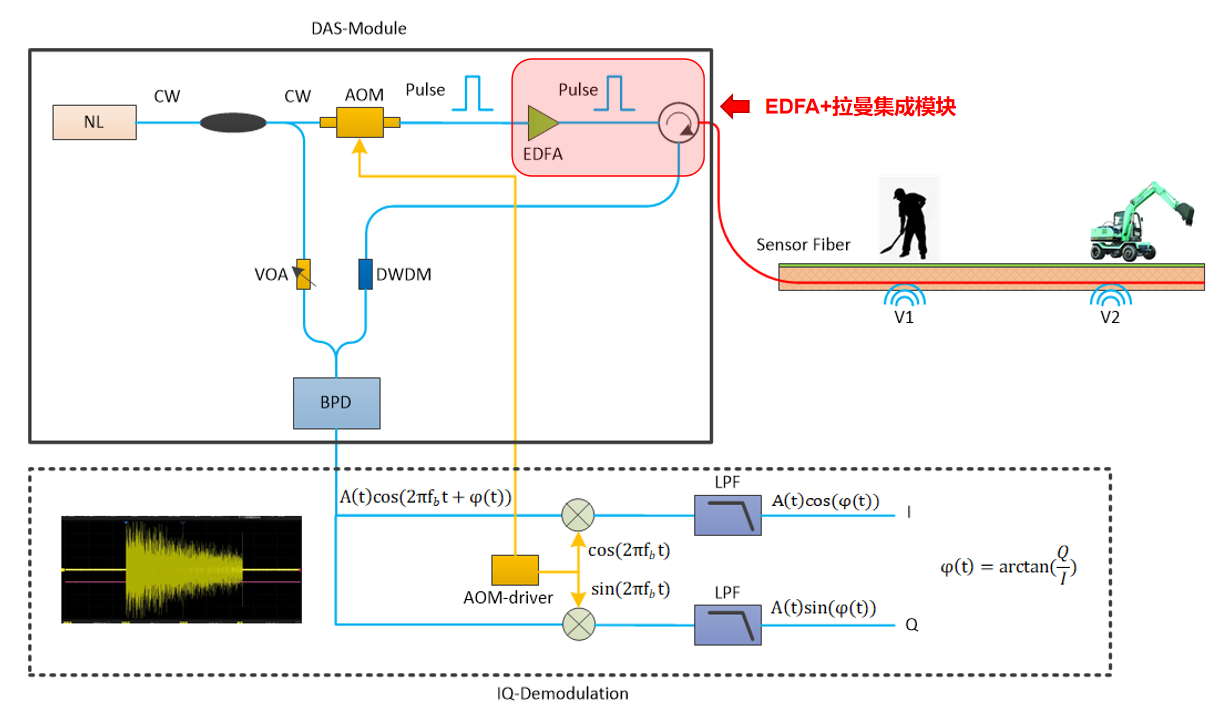
Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS) is an optical instrument that uses optical fiber as a sensor for sound vibration sensing. The system uses a single optical fiber to simultaneously monitor sound vibration and transmit the signal.
Distributed acoustic sensing (DAS) technology is an emerging sensing technology, which uses common single-mode communication fiber optic cable as a sensor to distribute physical parameter information at any point along the fiber, with the advantages of rich measurement information, precise positioning, and intrinsic safety.
DAS technology uses coherent detection, the phase is completely linear with the vibration, that is, to meet the event analysis and judgment, to provide quantitative information, greatly expanding the distributed acoustic sensing technology signal detection capabilities and applications, especially for oil and gas resources, transportation, marine geophysics, natural earthquakes, perimeter security field provides a new, effective and low-cost technology solutions, showing great application prospects It has been developed rapidly.
Distributed Acoustic Sensing Real-time Demodulation Demo Video
Distributed Acoustic Sensing Principle
The principle of distributed acoustic sensing system is to use the phase of coherent backscattered Rayleigh light rather than light intensity to detect signals such as sound vibrations in the audio range. Not only can the magnitude of the phase amplitude be used to provide information on the intensity of sound vibration events, but also linear quantitative measurements are used to achieve the acquisition of information on the phase and frequency of sound vibration events.
Distributed acoustic sensing schematic
Distributed acoustic sensing system components
Distributed Acoustic Sensing R&D Tips
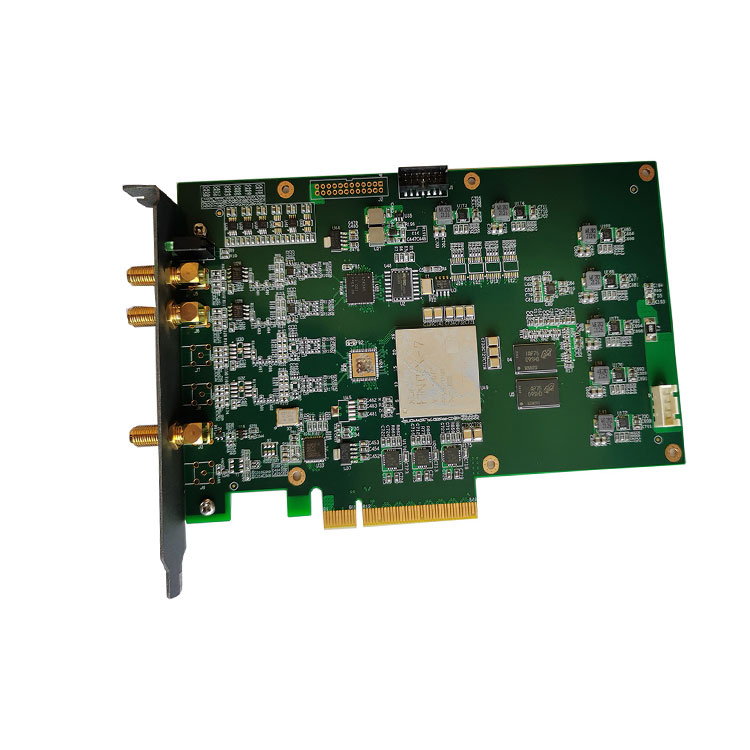
- Large data volume: Distributed acoustic sensing uses 80M acousto-optic modulator, 250MSps sampling rate of high-speed data acquisition card, the data volume will be very large, software processing large data volume is a challenge.
- IQ demodulation followed by phase unwinding: Distributed acousto-optic sensing demodulation requires IQ demodulation first, followed by phase unwinding, before the amplitude data and phase data can be obtained. Our DAQ card has built-in IQ demodulation function, but phase unwinding needs to be implemented in your software.
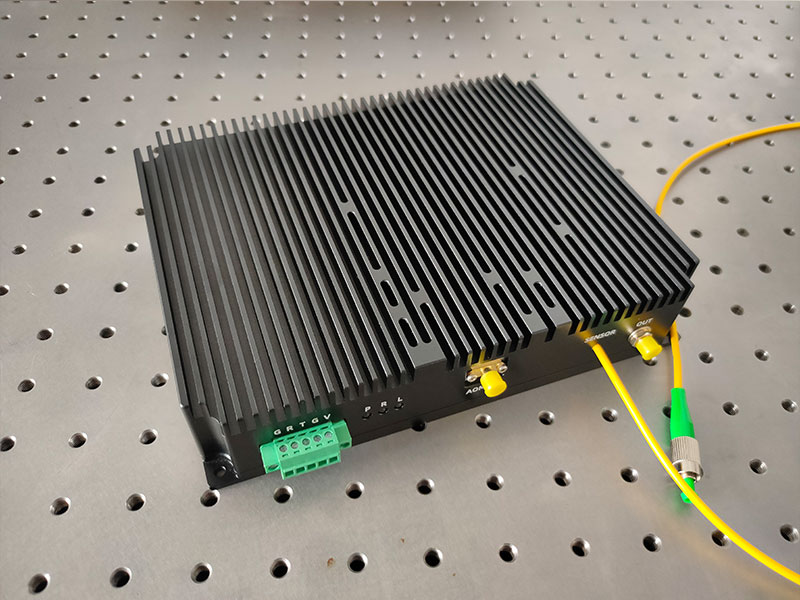
- R&D efficiency: If you focus on software demodulation, signal processing and algorithms for distributed acoustic sensing, we recommend you to use distributed acoustic sensing module because we have already integrated the laser, AOM, EDFA and BPD detectors. It saves you a lot of hardware development work.
- Key Applications of Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS) Systems Across Industries
- What kind of AOM should be used for DAS systems?
- What is the vibration response frequency of DAS?
- Spatial Resolution Of Distributed Acoustic Sensing
- What data acquisition card is needed for distributed acoustic sensing?
- EDFA for distributed acoustic sensing
- Balanced photodetectors for distributed acoustic sensing